- History of the Syrian Desert
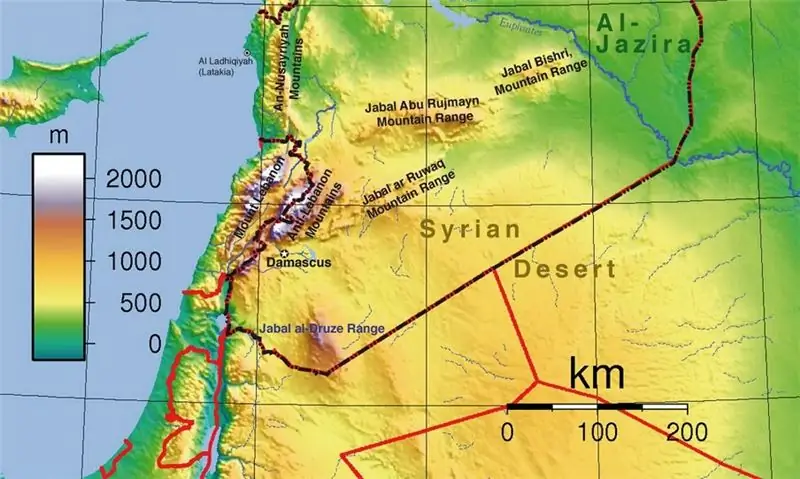
- Geographical position
- Syrian Desert Climate and Precipitation
- Flora and fauna
- At the crossroads
- Video
The Middle East region is characterized not only by a tense political situation, it is hot in the literal sense of the word, thanks to climatic and weather conditions. Many territories are occupied by deserts, one of them is the Syrian Desert, the second name is the Syrian Steppe.
It is interesting that the toponym contains the name of only one of the states, although the territory of the desert, except for Syria, occupies part of Iraq, Saudi Arabia and Jordan. Sandy areas alternate with steppe, therefore it is possible to use equally the definitions of "desert" and "steppe".
History of the Syrian Desert
Geographic maps show that the Syrian Desert covers an area of about 1 million square kilometers, it is a huge area of land. Its appearance is associated with the last glaciation, which ended 12 thousand years ago. For centuries, the lands were completely uninhabited, there were no people willing to develop them and somehow use them in economic activities.
The population explosion and the emergence of nomads who were engaged in cattle breeding helped. People were faced with a situation when it was necessary to develop new territories, albeit with such difficult conditions. It is believed that the first inhabitants of the territories now occupied by the Syrian Desert were the Amorites. Then they were replaced by representatives of the Aramaic civilization, followed by the Arabs. Today, most of the local population is Bedouin, they speak different Arabic dialects.
Geographical position
Semi-desert and desert areas occupy lands that lie at the junction of the Arabian Peninsula and the so-called Fertile Crescent. The desert is bounded by the following geographic features: the Euphrates River - from the northeast; the Mediterranean coast - from the west.
In the southern and southwestern regions, it is difficult to draw a border, because the Syrian steppe smoothly turns into the Nefud and Negev deserts. The central river Euphrates, to which numerous wadis are directed, water flows periodically, during the precipitation season, the rest of the time the channels are dried up.
The relief of the desert is dominated by plateaus with a flat surface. In some places, you can see the island mountains, the height of which is 1000 meters. The soil is heterogeneous; there are limestones, silicon, salt marshes (in depressions of the relief) and takyrs.
Syrian Desert Climate and Precipitation
Geographers note that these territories are located in the subtropical zone. The weather is warm enough, in winter the thermometers are kept at + 7 ° С (average January temperature), but every year on some days, frosts are noted on the soil.
In summer - about + 30 ° С. There is little precipitation, it falls unevenly, the amount of precipitation in the southern and northern regions of the desert differs significantly. The closer to the southeast, the fewer of them. In the north and northwest, the norm is about 200-300 mm, in the south - only 50-80 mm.
Flora and fauna
This is not to say that the Syrian desert is completely devoid of vegetation, but the statement about a solid green cover would be just as wrong. Among the representatives of the flora kingdom, the most common are shrubs and grasses.
It is clear that saxaul, which survives in the most severe conditions, cannot be done without saxaul. Another popular shrub in these places is biyurgun, the second name is the salt marsh barnyard. Among the herbs, wormwood predominates, but it appears in winter, after precipitation. Ephemera and their "colleagues", ephemeroids, are widespread, only such plants are able to withstand high temperatures and lack of moisture.
It is known that in the century before last, there were quite a few species of various animals in the Syrian desert. Unfortunately, the man mercilessly hunted and destroyed our smaller brothers. Historians say that earlier one could see ostriches, dromedary camels, onagers and lions.
At the crossroads
The Syrian desert has been at the crossroads of various roads since time immemorial, connecting the Mediterranean coast with Mesopotamia. It was here that the famous caravan route ran, on the way of which oases and famous historical cities, such as Damascus or Palmyra, were located.
Today, high-speed highways are laid across the territory, and desert ships, handsome camels, can be found extremely rarely, caravans are becoming a unique, exotic phenomenon.
Oases are the exact opposite of the desert, a world of greenery, water and coolness. Viticulture, horticulture are actively developing here, cotton and subtropical crops, date groves are planted. The same goes for the Mediterranean coast, which is the main citrus growing region. The Euphrates Valley preserves small floodplain forests consisting of tamarisk and willow.






